When you experience a cut or scrape, your blood clots to protect the wound, preventing excessive bleeding and keeping bacteria out. Inside your body, blood clots serve the same protective function by repairing damaged blood vessels.
However, blood clots can also form in places where they shouldn’t, leading to serious health risks. When a clot obstructs blood flow in your veins or arteries, it can cause life-threatening complications. A blood clot ultrasound of your leg helps detect and diagnose these issues early.
What Happens When Blood Clots Block Arteries?
The symptoms and consequences of blood clots vary depending on whether they form in arteries or veins.
Blood Clots in Arteries
Clots in arteries can block oxygen-rich blood from reaching vital organs, leading to severe medical conditions such as:
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): If a clot obstructs an artery supplying blood to the heart, the heart muscle can begin to die. Symptoms include:
- Chest pain
- Upper body discomfort
- Nausea and fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): If a clot blocks an artery supplying the brain, brain cells may die due to lack of oxygen. Symptoms include:
- Numbness or weakness on one side of the body
- Facial drooping
- Slurred speech
Both conditions require immediate medical intervention to prevent permanent damage or death.
What Happens When Blood Clots Block Veins?
Clots forming in veins present different risks, though they are just as dangerous.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
- DVT occurs when clots develop in deep veins, particularly in the legs.
- The inferior vena cava, the major vein carrying deoxygenated blood from the lower body to the heart, is a common site for these clots.
- Many patients with DVT do not experience symptoms, but possible signs include:
- Pain
- Warmth
- Redness
- Swelling
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
- If a DVT clot breaks free and travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism.
- Symptoms include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid heartbeat
- Dizziness
Both DVT and PE require immediate treatment, as they can be life-threatening.
Risk Factors for Blood Clots
Several factors increase the risk of blood clots, including:
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking and prolonged immobility (long flights, car rides, or bed rest after surgery) contribute to clot formation.
- Hormonal Factors: Birth control pills and hormone therapy may increase the risk, but the benefits often outweigh the risks.
- Pregnancy: Increases blood clot risk due to changes in circulation.
- Vein Disease: Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI) and Venous Stasis occur when the one-way valves in veins weaken. This leads to:
- Blood pooling in the legs
- Increased pressure in veins
- Varicose veins and spider veins
- Leg cramps and heaviness
If you have CVI or Venous Stenosis, you are at a higher risk for blood clots. For diagnosis and treatment, consult a vein specialist in New Jersey, California, Maryland or New York.
How Are Blood Clots Diagnosed?
If your doctor suspects a clot, they may order:
- Blood Tests
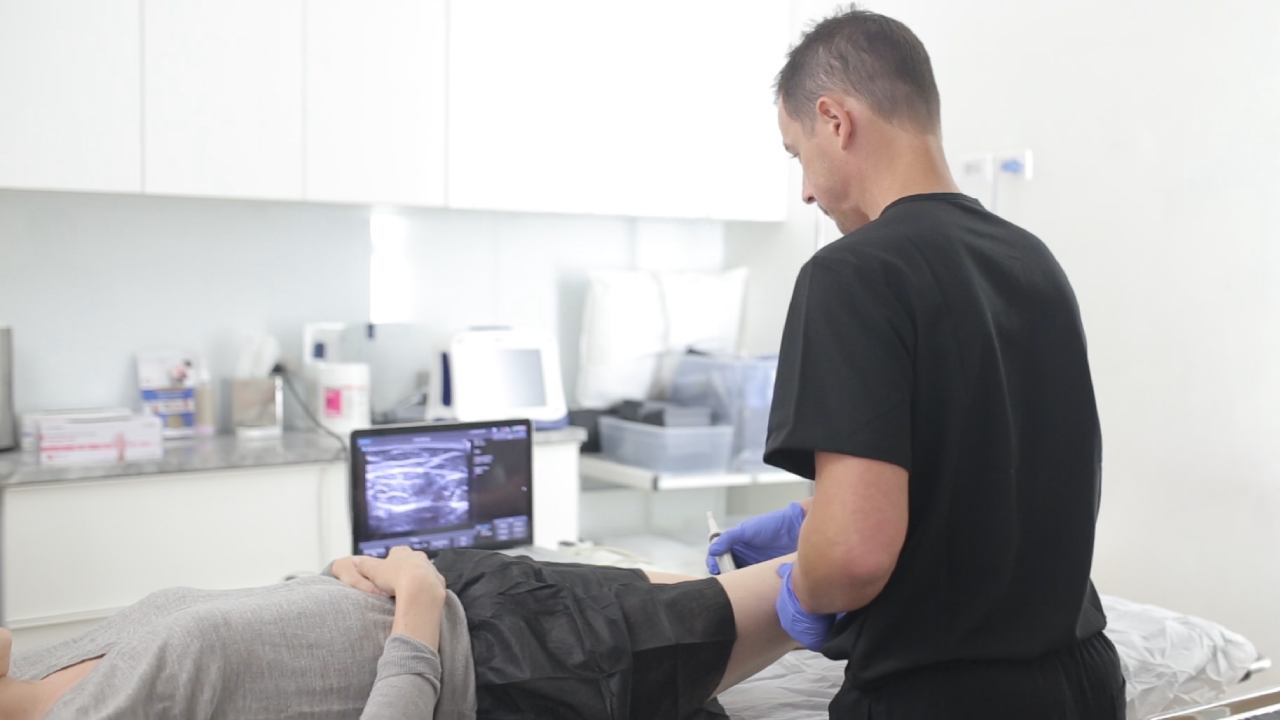
- Blood Clot Ultrasound (Doppler Ultrasound Imaging)
This non-invasive imaging test allows specialists to detect clots in real-time. It is painless, quick, and essential for assessing clot risks and determining treatment options.
How Are Blood Clots Treated?
Early Diagnosis and Treatment
- Blood thinners help prevent and dissolve clots if diagnosed early.
- If untreated, clots may travel to the heart, brain, or lungs, causing permanent disability or death.
Treating Underlying Vein Disease
Minimally invasive vein treatments can correct the issue if vein disease contributes to your clot risk. Our Vein Treatment Clinics offers:
- Sclerotherapy
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA)
- Venaseal
- Clarivein
- Varithena
These outpatient procedures redirect blood flow to healthier veins, improving circulation and preventing future clots.
How Can You Prevent Blood Clots?
- Stay Active: Move frequently, especially during long trips.
- Wear Compression Stockings: Reduce swelling and encourage circulation.
- Quit Smoking: Reduces clot risk and improves vascular health.
- Manage Medical Conditions: Work with your vein doctor to treat underlying issues like CVI and varicose veins.
Final Thoughts
Blood clots are treatable when diagnosed early. If your doctor ordered a blood clot ultrasound for your leg, following through with the evaluation is crucial. If you are at risk due to vein disease, pregnancy, or immobility, schedule a consultation with Vein Treatment Clinic into explore minimally invasive vein treatments that improve circulation and reduce clot risks.