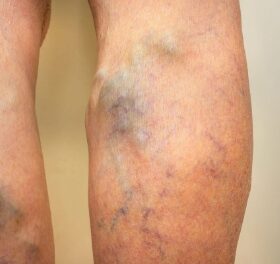
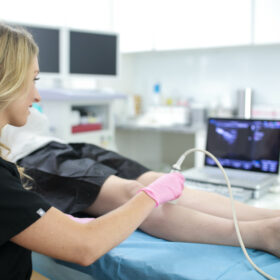
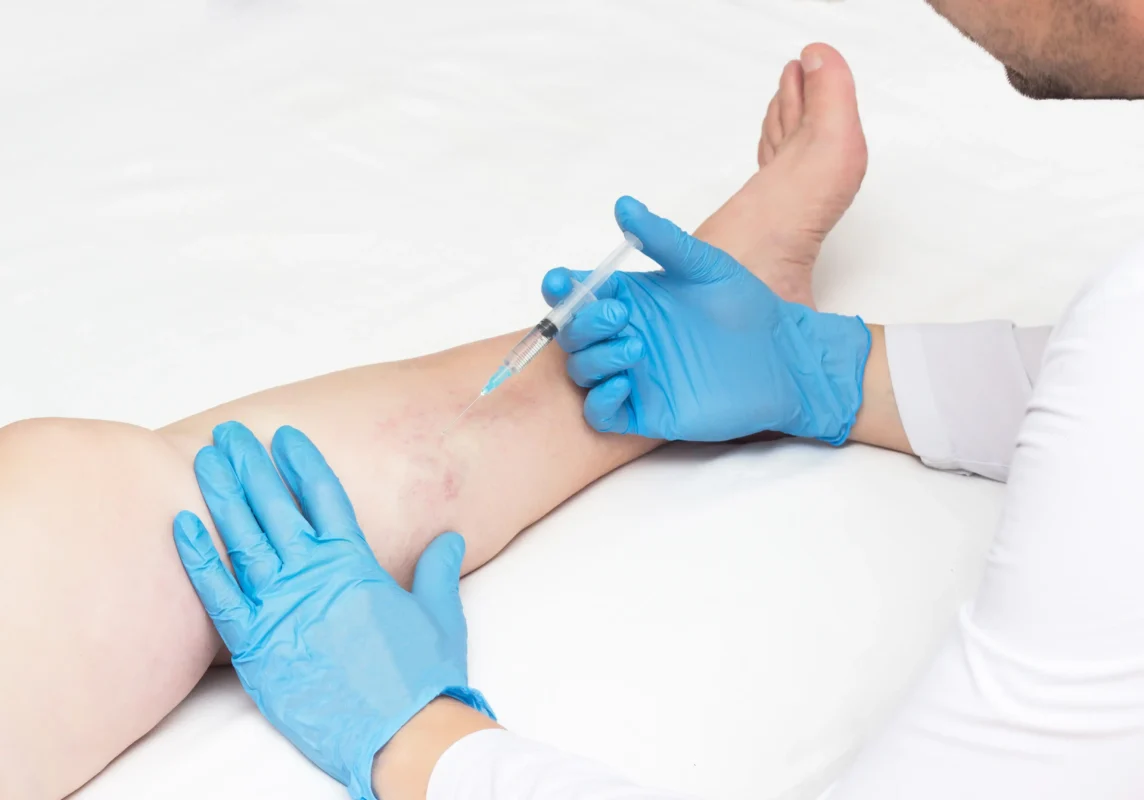
Vein stripping is a surgical procedure that removes varicose veins from the legs. The procedure has been around for decades and has evolved over time to become less invasive. This article will answer some of the most frequently asked questions about vein stripping, including how long the procedure takes, what to expect during recovery, and why you should opt for minimally invasive varicose vein treatments instead.
Vein Treatment Clinic is a group of luxurious, state-of-the-art vein clinics specializing in cutting-edge minimally invasive spider vein and varicose vein treatments. Instead of offering surgical procedures that involve extended downtime, such as vein stripping, we offer safer and more effective minimally invasive treatments, such as radiofrequency ablation and endovenous laser ablation. You can find our vein clinics in Long Island, New York, California, New Jersey, and Maryland. Please schedule an appointment at your nearest vein treatment clinic.
How long does a vein stripping procedure take?
A vein stripping procedure typically takes about 1 to 2 hours to complete. The exact duration of the procedure will depend on the number and size of the veins being treated, as well as the patient’s overall health. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and requires an overnight stay in the hospital. After the procedure, patients will need to wear compression stockings and avoid strenuous activity for several weeks for proper healing.
What are the drawbacks of vein stripping compared to minimally invasive varicose vein treatments?
The drawbacks of vein stripping compared to minimally invasive varicose vein treatments include:
- Recovery Time: Vein stripping requires a longer recovery time, typically several weeks, compared to minimally invasive treatments that only require a few days of recovery.
- Pain and Discomfort: Vein stripping is a more invasive procedure and can result in more pain and discomfort compared to minimally invasive treatments.
- Scarring: Vein stripping can result in noticeable scarring, whereas minimally invasive treatments leave little to no scarring.
- Risks: Vein stripping is associated with a higher risk of complications compared to minimally invasive treatments, such as bleeding, infection, and deep vein thrombosis.
- Incisions: Vein stripping may require multiple incisions, whereas minimally invasive treatments, such as endovenous laser therapy (EVLT) or radiofrequency closure, usually only require one or two small incisions.
- Underlying Disease: Another drawback of vein stripping is that it only treats the large superficial veins, and does not address the underlying cause of the varicose veins. Minimally invasive treatments, on the other hand, are designed to treat the underlying cause of the varicose veins, helping to prevent recurrence in the future.
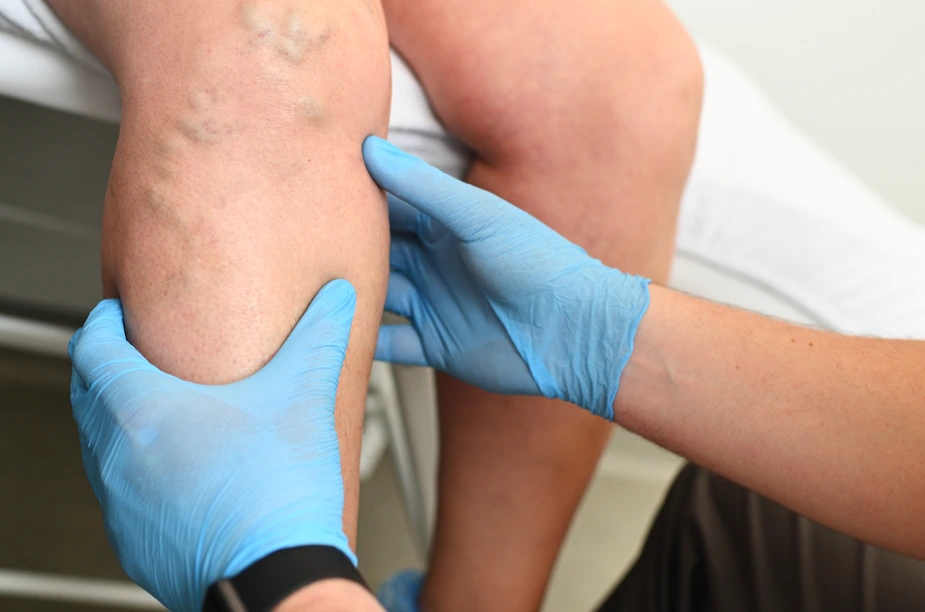
Should I get my varicose veins treated?
Yes, it is recommended to undergo a diagnosis if you have varicose veins because they can be symptomatic of underlying chronic venous insufficiency, a condition in which the veins have trouble sending blood back to the heart. Chronic venous insufficiency can lead to serious health problems if left untreated, including blood clots, skin damage, and ulcerations.
Additionally, varicose veins can also cause physical discomfort, such as pain, swelling, and fatigue in the legs. Treating the underlying condition and relieving the symptoms can improve your quality of life and prevent further complications. You can also undergo varicose vein treatments for cosmetic reasons to make your legs look smooth and restore their beauty.
What are the signs of blood clot after vein ablation?
The signs of a blood clot after vein ablation, also known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), include:
- Swelling in the affected leg: A blood clot can cause swelling and tenderness in the affected leg.
- Pain or tenderness: A blood clot can cause aching or painful sensations in the affected leg.
- Warmth to the touch: The affected leg may feel warm to the touch due to increased blood flow and inflammation.
- Redness or discoloration: The affected leg may have red or discolored skin due to increased blood flow and inflammation.
- Rapid pulse: A blood clot can cause an increased pulse rate in the affected leg.
If you experience any of these symptoms after vein ablation, it is important to seek medical attention immediately as DVT can be serious and even life-threatening if left untreated. Your healthcare provider can perform diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of a blood clot and recommend appropriate treatment to prevent further complications.
When should I contact a doctor to remove varicose veins?
You should contact a doctor to remove varicose veins when they cause:
- Pain: If you experience discomfort, aching, or pain in your legs due to varicose veins, it may be time to seek treatment.
- Swelling: If you experience swelling in your legs, particularly at the end of the day, it may be a sign of underlying venous insufficiency and a reason to seek treatment.
- Skin changes: If you notice changes in the color or texture of your skin near your varicose veins, it may be time to seek treatment.
- Ulcerations: If you have open sores near your varicose veins, it is important to seek treatment to prevent further complications.
- Bleeding: If you experience spontaneous bleeding from your varicose veins, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
What happens during RF ablation for varicose veins?
Radiofrequency (RF) ablation is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat varicose veins. During the procedure, the following steps occur:
- Local anesthesia: The procedure is performed under local anesthesia to numb the treatment area.
- Insertion of a catheter: A thin catheter is inserted into the diseased vein through a small incision.
- Heating of the vein: Radiofrequency energy is transmitted through the catheter to heat the vein, causing the vein walls to collapse and seal shut.
- Removal of the catheter: The catheter is then removed, leaving behind a closed vein.
- Blood rerouted: Blood flow is redirected to other healthy veins.
The entire procedure typically takes about 30-60 minutes and can be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day. After the procedure, patients may experience some discomfort, but this usually resolves within a few days. Most patients can return to normal activities immediately, although it is recommended to avoid strenuous activities for several weeks to allow the treated veins to fully heal.