What is CVI in medical terms?
Venous insufficiency, also known as chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), is a medical condition in which the veins in the legs cannot adequately pump blood back to the heart. This results in the pooling of blood in the legs, leading to swelling, pain, and other symptoms. CVI is caused by damage or dysfunction of the valves in the veins, which normally keep blood flowing in one direction. When these valves are damaged or not functioning properly, blood can flow backward, causing it to accumulate in the veins. This can lead to swelling and other symptoms.
What are the early symptoms of venous insufficiency?
The early symptoms of CVI may include:
- Swelling in the ankles and legs
- Leg heaviness and pain
- Frequent leg cramps
- Restless leg syndrome
- Aching or pain in the legs, especially after standing or sitting for long periods of time
- Skin changes, such as redness, discoloration, or thickening
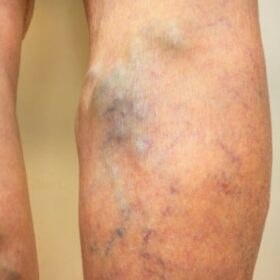
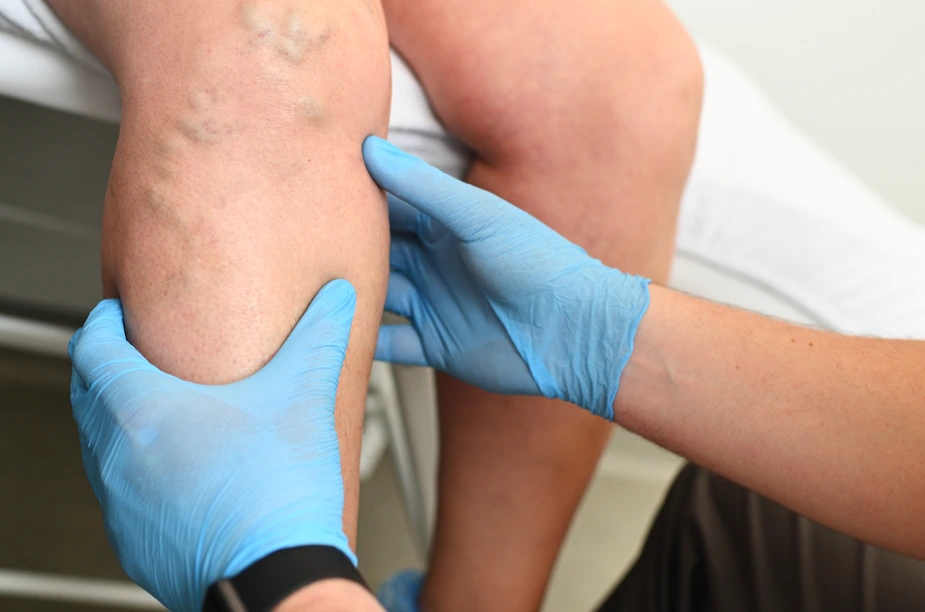
- Varicose veins, which are swollen, twisted veins that are visible through the skin
If you experience these symptoms, you must see a vein doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Our state-of-the-art vein treatment clinics are led by board-certified vein doctors who diagnose and treat the root cause of varicose veins and spider veins. Our vein doctors diagnose chronic venous insufficiency before addressing the symptoms, ensuring safe results.
You can find our vein doctors and vein treatment clinics in Long Island, New York City, New Jersey, California, and Maryland. If you’re in California, our vein clinics are in San Jose and San Diego. Please schedule an appointment at your nearest vein treatment clinic.
What are the long-term complications of untreated chronic venous insufficiency?
If CVI is not treated, it can lead to several serious complications, including:
- Skin changes, such as discoloration, ulcers, or thickening
- Blood clots, which can be dangerous if they break free and travel to the lungs or other organs
- Cellulitis, a bacterial infection of the skin and underlying tissue
- Lymphedema, a condition in which fluid builds up and causes swelling in the legs and ankles
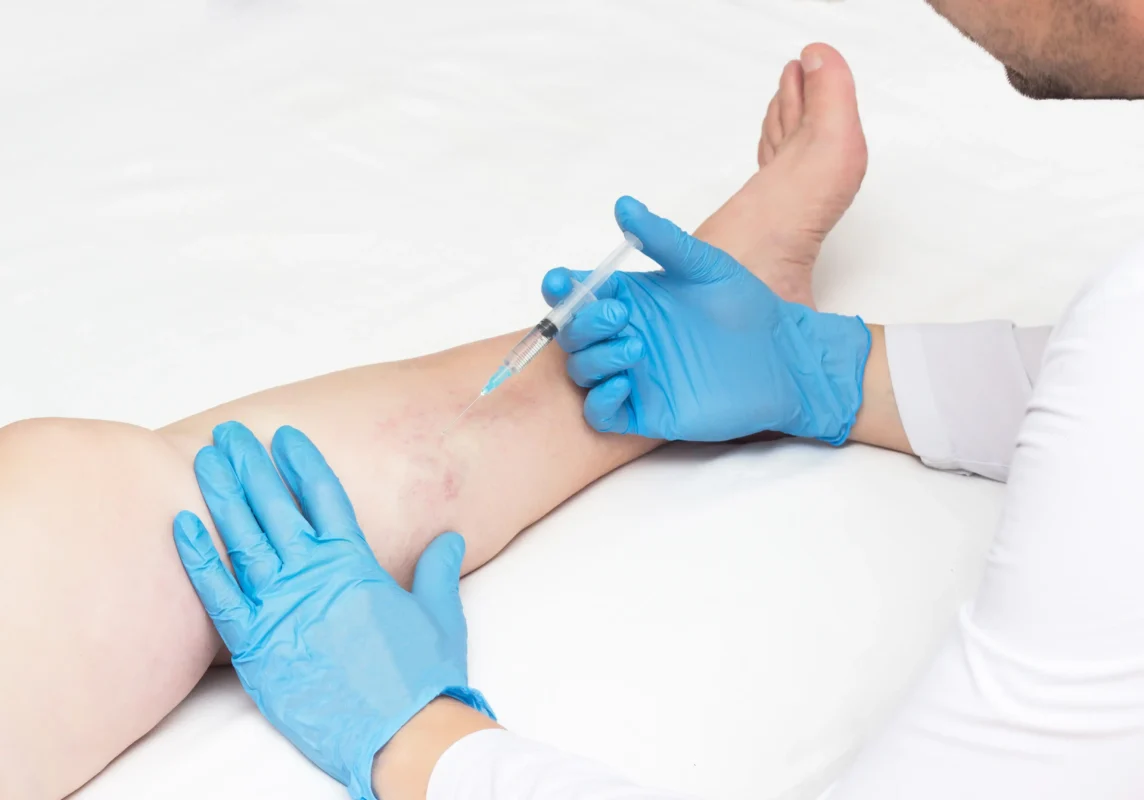
It is important to seek treatment for CVI as soon as possible to avoid these complications. Our vein doctors use cutting-edge imaging tests, such as duplex ultrasound, to visualize the direction of blood in your leg veins and curate a personalized treatment plan consisting of minimally invasive procedures, such as radiofrequency ablation and venaseal.
What are the risk factors for CVI?
Several risk factors can increase your risk of developing CVI, including:
- Age: CVI is more common in older adults
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop CVI than men
- Family history: If you have a family history of CVI, you may be at increased risk
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of CVI
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy can cause temporary CVI, which usually resolves after delivery
- Standing or sitting for long periods of time: This can put pressure on the veins in the legs and increase your risk of CVI
How can I reduce the risk of venous insufficiency?
There are several things you can do to reduce your risk of CVI:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of CVI, so it is important to maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Exerciseregularly: Regular physical activity can improve circulation and reduce the risk.
- Elevate your legs: When sitting or lying down, try to elevate your legs above the level of your heart to improve circulation.
- Wear compression stockings: These special stockings apply gentle pressure to the legs, which can improve circulation and reduce the risk of CVI.
- Don’t stand or sit for long periods of time: If you work a job that requires you to stand or sit for long periods of time, take breaks and move around as often as possible.
Does high blood pressure cause varicose veins?
High blood pressure is not known to be a direct cause of varicose veins. But, what is known is that one of the common consequences of high blood pressure is weakened or damaged veins. These weakened or damaged veins can contribute to the development of varicose veins, suggesting that this is an indirect cause. It’s important to talk to your vein doctor if you have high blood pressure because it could increase your risk of varicose veins.
How is venous insufficiency diagnosed?
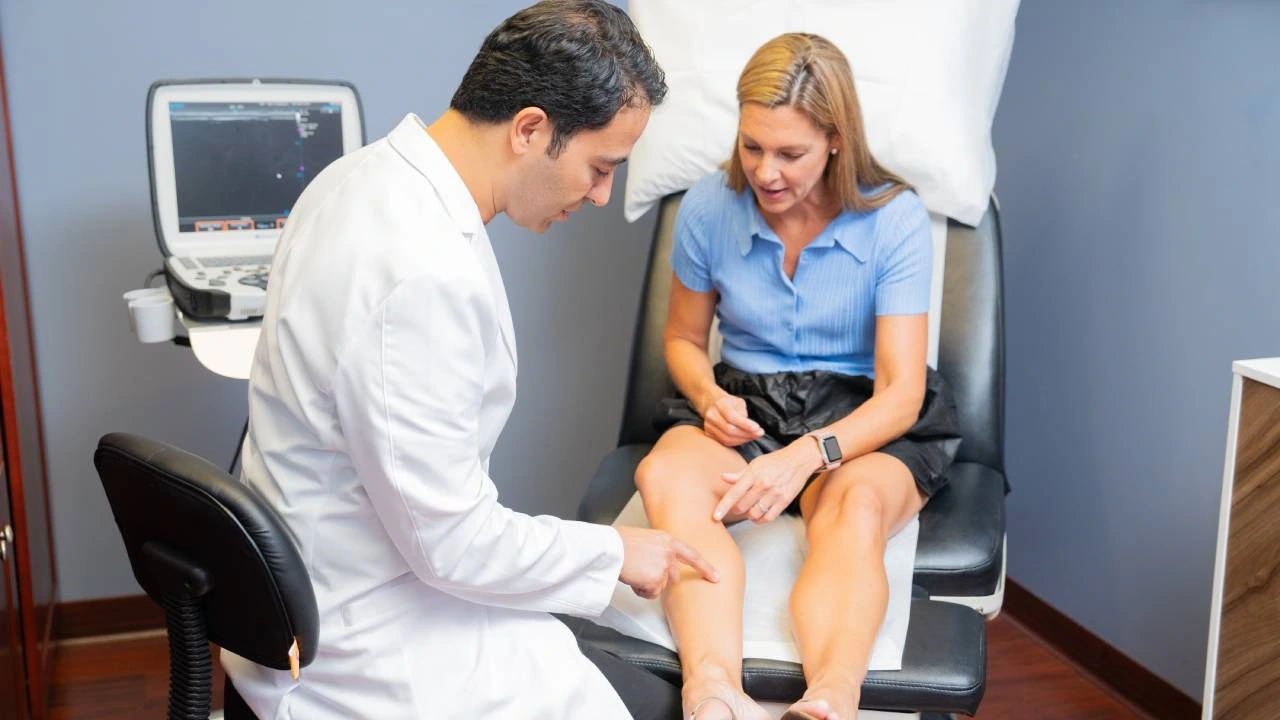
Venous insufficiency, or chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), is typically diagnosed through a combination of a medical history check, a discussion of your symptoms, a physical examination, and diagnostic tests. During the medical history check, the vein doctor will ask about your personal and family medical history and any current symptoms you are experiencing, such as swelling in the legs and ankles, pain or aching in the legs, and skin changes. These symptoms can be indicative of CVI, but they can also be caused by other conditions, so further testing is often necessary.
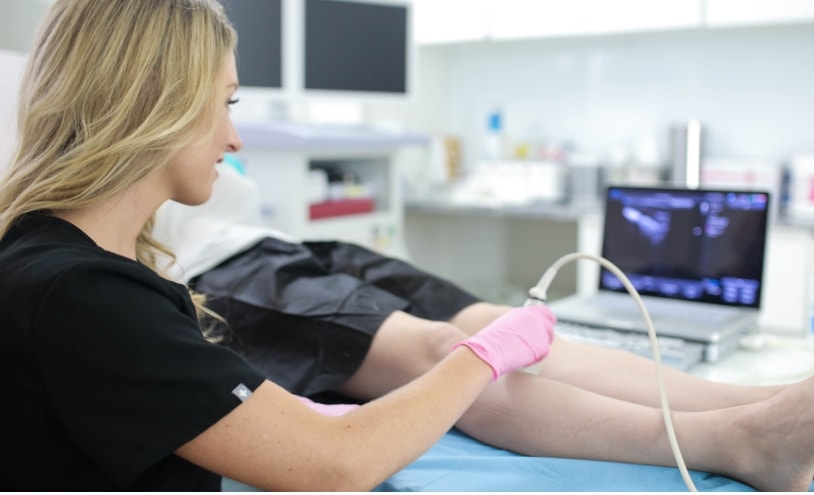
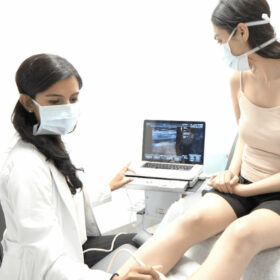
One of the most common tests used to diagnose CVI is a duplex ultrasound test. This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create a detailed image of the veins in the legs. It can identify any damage or dysfunction of the valves in the veins and any blood clots or other abnormalities. Our vein doctors carefully examine the direction of blood flow in your leg veins to determine if you have chronic venous insufficiency and curate an appropriate treatment plan, which may include endovenous laser ablation, radiofrequency ablation, venaseal, and other minimally invasive procedures.